The Relationship Between Smoking and Diabetes
Smoking and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
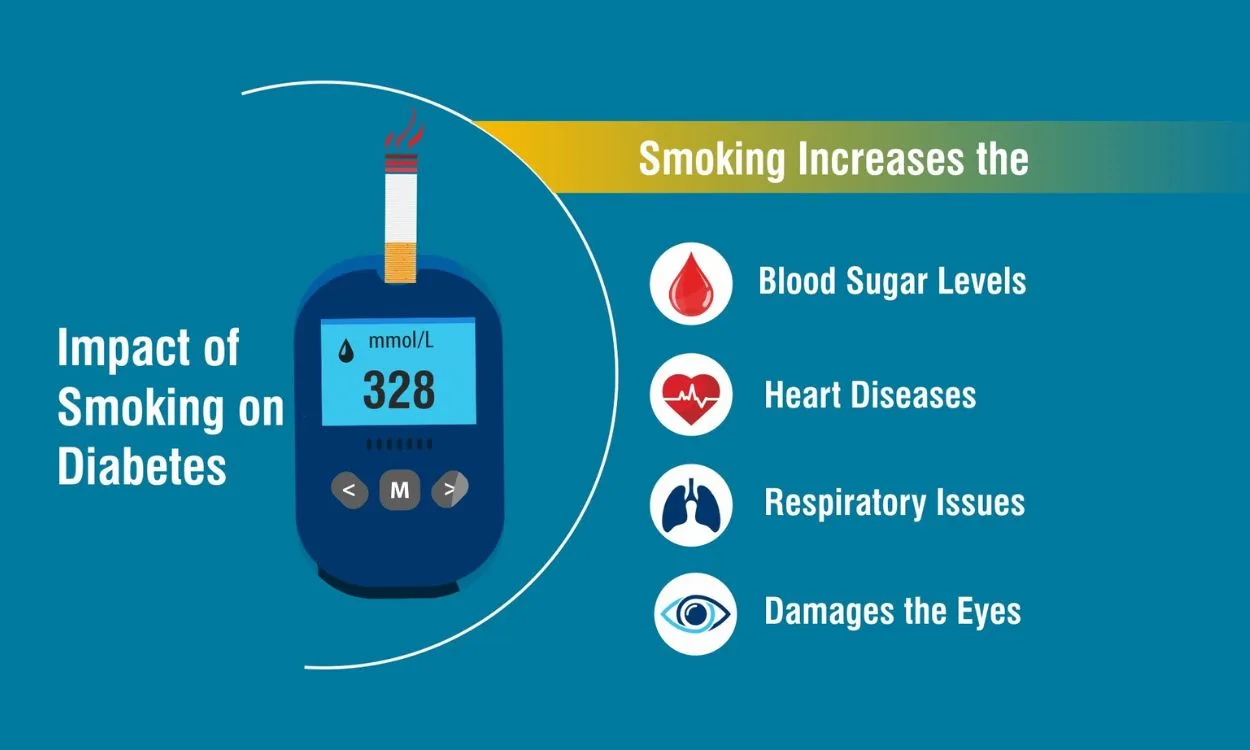
- Smoking is a significant risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes.
- The toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke impair the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar and insulin levels, leading to insulin resistance and increased blood sugar levels.
- Studies have shown that smokers are 30-40% more likely to develop type 2 diabetes compared to non-smokers.
Impact of Smoking on Insulin Sensitivity
- Smoking negatively affects insulin sensitivity, making it harder for the body to respond to insulin, leading to higher blood sugar levels.
- Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes can cause inflammation and oxidative stress in the body, further contributing to insulin resistance.
Smoking and Diabetes Complications
- For individuals with diabetes, smoking exacerbates the risk of complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems.
- Smoking also impairs the body’s ability to heal, which can worsen diabetic foot ulcers and other wounds.
Secondhand Smoke and Diabetes Risk
- Exposure to secondhand smoke has also been linked to an increased risk of type 2 diabetes, particularly in nonsmoking adults.
- Secondhand smoke contains many of the same harmful chemicals as directly inhaled smoke, contributing to insulin resistance and other diabetes-related risks.
The Link Between Smoking and Gestational Diabetes
- Smoking During Pregnancy and Gestational Diabetes
- Smoking during pregnancy is associated with a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes.
- The toxic effects of smoking on insulin sensitivity and blood sugar regulation can contribute to the development of gestational diabetes in pregnant women.
Impact on Maternal and Fetal Health
- Gestational diabetes increases the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby, and when combined with smoking, the risks are further heightened.
- Smoking during pregnancy can lead to low birth weight, preterm birth, stillbirth, and other adverse outcomes, especially in the presence of gestational diabetes.
Smoking Cessation and Diabetes Management The Fitpaa App – Transforming Health and Fitness
Benefits of Quitting Smoking for Individuals with Diabetes
- Quitting smoking has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control, reducing the risk of diabetes complications.
- Smoking cessation can lead to a significant decrease in cardiovascular risk, which is particularly important for individuals with diabetes who are already at higher risk for heart disease.
Challenges and Support for Quitting Smoking
- Individuals with diabetes may face additional challenges when quitting smoking, as nicotine withdrawal can temporarily affect blood sugar levels and insulin requirements.
- Support from healthcare professionals, cessation programs, and behavioral interventions can help individuals with diabetes successfully quit smoking while managing their diabetes effectively.
Fitpaa’s Mission for a Healthier India
- Fitpaa is dedicated to empowering individuals to achieve their health and fitness goals, including managing conditions like diabetes, through personalized, evidence-based plans.
- With a focus on promoting overall wellbeing and disease management, Fitpaa aims to transform the health and fitness landscape in India.
Fitpaa’s Approach to Diabetes Management
- Fitpaa offers specialized support for individuals with diabetes, including tailored nutrition and exercise plans to optimize blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications.
- The Fitpaa app provides real-time guidance, personalized coaching, and access to a comprehensive healthcare team to support individuals in their diabetes management journey.
Guaranteed Results and Supportive Community
- Fitpaa’s commitment to guaranteed results and lifetime validity of services aligns with the long-term goals of individuals managing diabetes and seeking sustainable health improvements.
- The Fitpaa community fosters motivation, accountability, and ongoing support, creating a positive environment for individuals to take charge of their health and wellbeing.