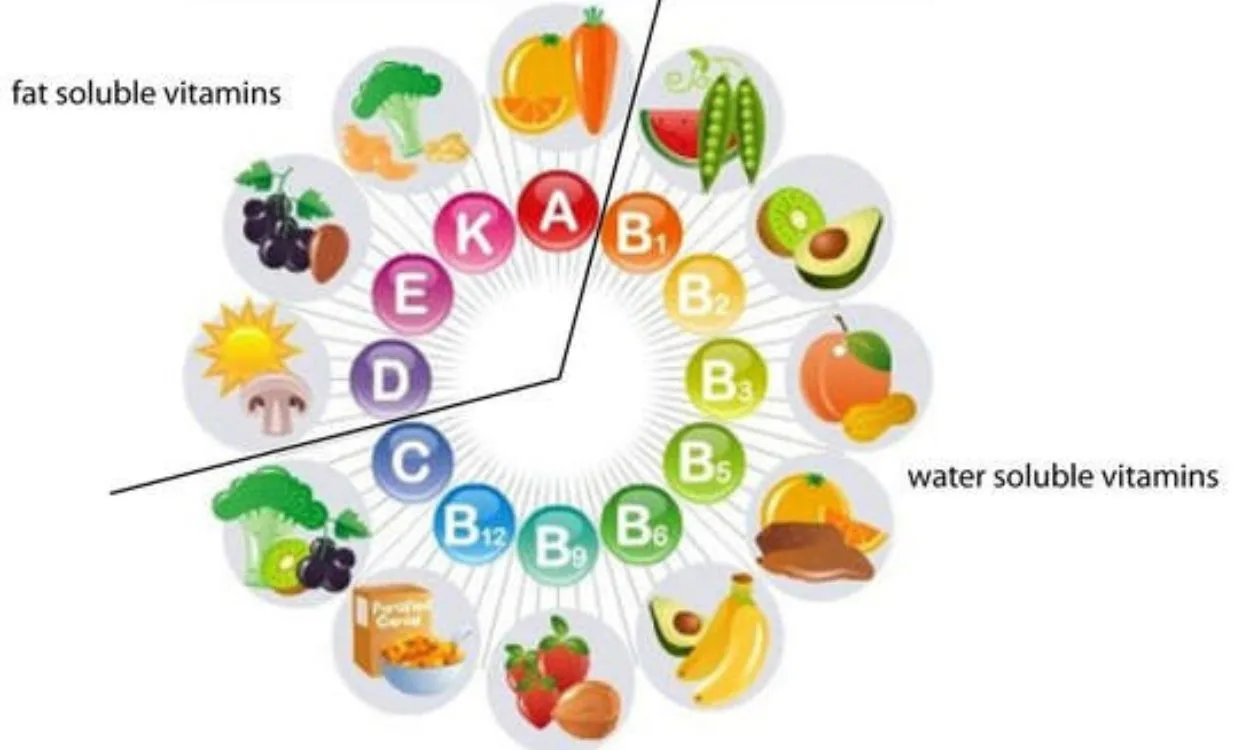
What is the difference between water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins?
Vitamins are essential nutrients that our bodies need to function properly. They play a crucial role in maintaining good health and preventing various diseases. Vitamins can be categorized into two main groups: water-soluble vitamins and fat-soluble vitamins. Understanding the difference between these two types of vitamins is important to ensure that we meet our daily nutritional requirements.
Water-Soluble Vitamins
Water-soluble vitamins are a group of vitamins that dissolve in water. This means that they are easily absorbed by the body and any excess amounts are excreted through urine. The water-soluble vitamins include vitamin C and the B-complex vitamins (thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, pyridoxine, biotin, folic acid, and cobalamin).
Here are some key characteristics of water-soluble vitamins:
- Absorption and Storage: Water-soluble vitamins are quickly absorbed in the small intestine and transported to various tissues in the body. Unlike fat-soluble vitamins, the body does not store water-soluble vitamins, so they need to be replenished regularly through diet.
- Function: Water-soluble vitamins play crucial roles in energy metabolism, immune function, collagen synthesis, and the production of red blood cells. They are also involved in maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails, as well as supporting brain function and overall well-being.
- Food Sources: Good sources of water-soluble vitamins include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and fortified foods. These vitamins are sensitive to heat, light, and air, so it’s important to handle and cook these foods properly to retain their vitamin content.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins
Unlike water-soluble vitamins, fat-soluble vitamins cannot dissolve in water. Instead, they require fat for proper absorption and transport in the body. The fat-soluble vitamins include vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Here are some key characteristics of fat-soluble vitamins:
- Absorption and Storage: Fat-soluble vitamins are absorbed along with dietary fat in the small intestine and are transported through the lymphatic system. Unlike water-soluble vitamins, the body can store fat-soluble vitamins in fatty tissues and the liver. This allows the body to access them when needed, even if dietary intake is insufficient.
- Function: Fat-soluble vitamins are involved in various functions such as vision (vitamin A), calcium absorption and bone health (vitamin D), antioxidant protection (vitamin E), and blood clotting (vitamin K). They play a crucial role in maintaining the health of various organs and systems in the body.
- Food Sources: Good sources of fat-soluble vitamins include animal products (such as liver, eggs, and dairy) for vitamins A, D, and K, and plant-based oils, nuts, and seeds for vitamin E. It’s important to note that excessive intake of fat-soluble vitamins through supplements can lead to toxicity because they are stored in the body.
In conclusion, water-soluble vitamins are easily absorbed by the body, not stored in significant amounts, and need to be replenished regularly through diet. On the other hand, fat-soluble vitamins require dietary fat for absorption, can be stored in the body, and should be consumed in moderation to avoid toxicity. Both types of vitamins play important roles in maintaining good health, and a balanced diet that includes a variety of food sources can help ensure adequate intake of both water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins.
If you are looking for a comprehensive health and fitness solution, consider downloading the Fitpaa app. Fitpaa offers personalized fitness plans, nutrition guidance, and real-time monitoring to help you achieve your health and fitness goals. Take control of your well-being and start your journey towards a healthier life with Fitpaa.
Download the Fitpaa app now and take the first step towards a healthier you!