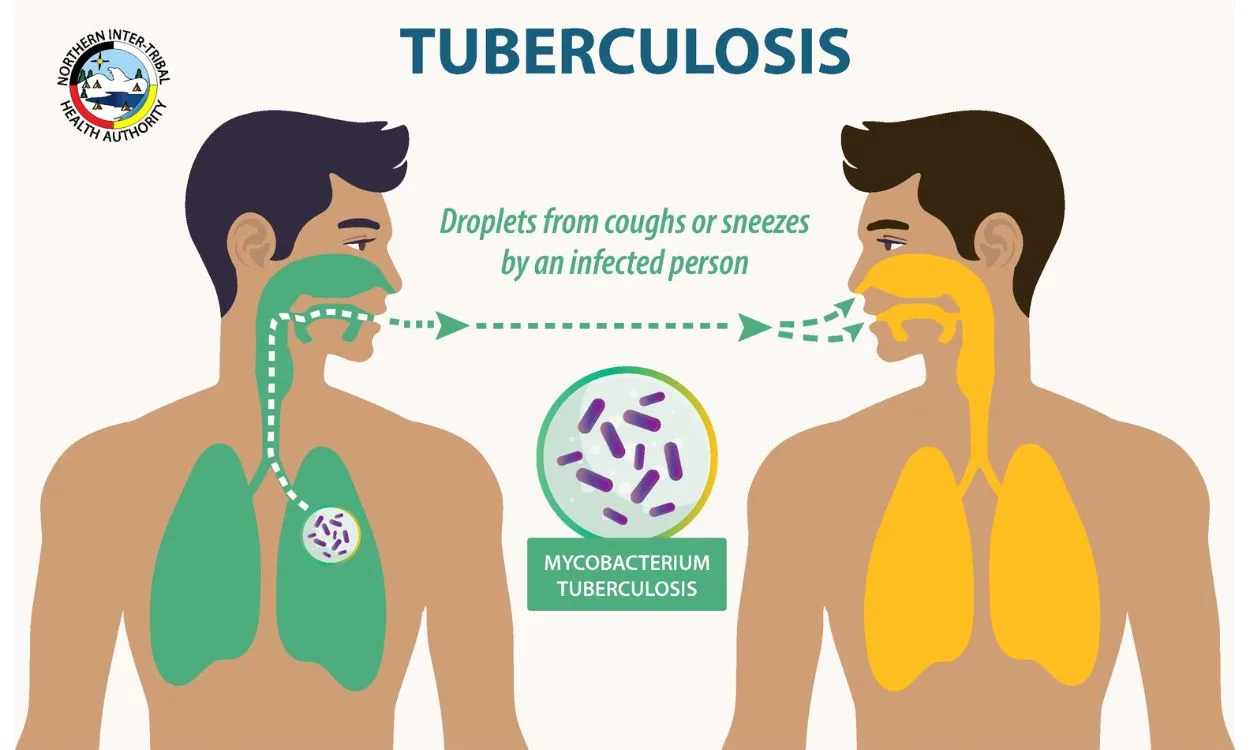
How is TB Transmitted?
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious airborne disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It primarily affects the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body such as the kidneys, spine, and brain. Understanding how TB is transmitted is crucial for preventing its spread.
Here is a detailed explanation of how TB is transmitted:
- Airborne Transmission: TB is primarily transmitted through the air when an infected individual coughs, sneezes, talks, or sings. The bacteria are released into the air in tiny droplets called aerosols. When a person inhales these aerosols containing the TB bacteria, they can become infected.
- Close Contact: Close and prolonged contact with an infected person increases the risk of transmission. This includes living in the same household, working together, or spending a significant amount of time in close proximity to an infected individual.
- Crowded and Poorly Ventilated Settings: TB transmission is more likely to occur in crowded places with poor ventilation, such as prisons, homeless shelters, and certain healthcare facilities. The bacteria can remain suspended in the air for an extended period, increasing the chances of inhalation by others.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with a weakened immune system, such as those with HIV/AIDS, malnutrition, diabetes, or certain cancers, are at a higher risk of developing active TB if they come into contact with the bacteria.
- Sharing of Personal Items: Although less common, TB can also be transmitted through the sharing of contaminated personal items such as respiratory equipment, toothbrushes, or drinking glasses. However, it’s important to note that casual contact, hugging, or shaking hands with an infected person does not typically lead to transmission.
Now that we understand how TB is transmitted, it is crucial to take preventive measures to control its spread:
- Early Diagnosis: Timely detection and diagnosis of TB cases can help prevent further transmission. Individuals with symptoms such as persistent cough, chest pain, fatigue, weight loss, and night sweats should seek medical attention and get tested for TB.
- Isolation and Treatment: Infected individuals should be isolated and started on appropriate treatment as soon as possible to minimize the risk of transmission. Completing the full course of treatment is essential to cure the infection and prevent the development of drug-resistant strains.
- Good Respiratory Hygiene: Covering the mouth and nose with a tissue or elbow when coughing or sneezing can help prevent the spread of TB bacteria. Proper disposal of used tissues and regular handwashing are also important.
- Ventilation and Airflow: Improving ventilation in crowded spaces, ensuring fresh air circulation, and maintaining good airflow can reduce the concentration of TB bacteria in the environment and lower the risk of transmission.
- Infection Control Measures: Healthcare facilities, correctional facilities, and other high-risk settings should implement effective infection control measures. This includes regular screening of individuals, proper use of personal protective equipment, and adherence to strict hygiene practices.
While it is crucial to understand and prevent the transmission of TB, it is equally important to prioritize overall health and well-being. Fitpaa, a comprehensive health and fitness app, can help you achieve your health goals and take proactive steps towards overall wellness. Download the Fitpaa app today and embark on a journey towards a healthier and happier life.