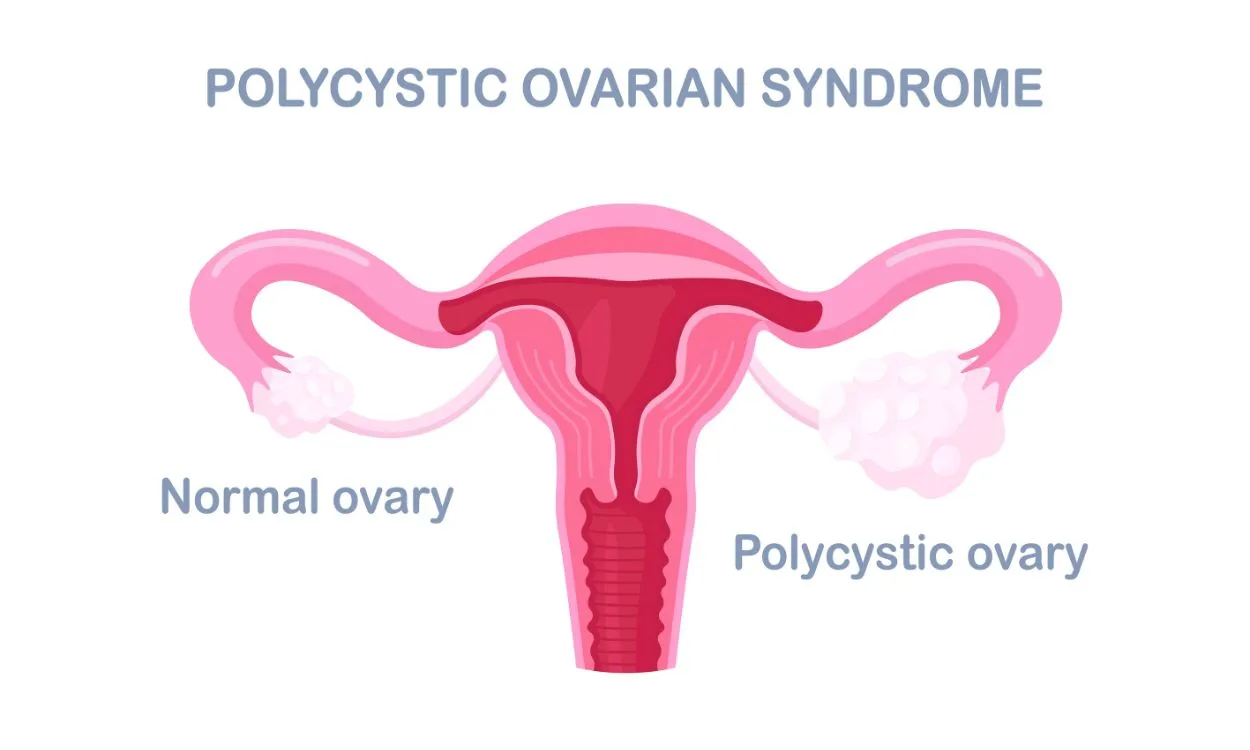
How does insulin resistance contribute to PCOD?
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body’s cells become less responsive to the hormone insulin, leading to an increase in blood sugar levels. This condition is commonly associated with type 2 diabetes, but it can also play a significant role in the development of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women. PCOS is a hormonal disorder that affects the ovaries and can lead to irregular periods, infertility, and other health complications.
Insulin resistance and PCOS are closely linked, and one can exacerbate the other. Here’s a detailed explanation of how insulin resistance contributes to PCOS:
- Elevated insulin levels: Insulin is responsible for regulating blood sugar levels and promoting the storage of glucose in cells for energy. In women with insulin resistance, the body produces higher levels of insulin to compensate for the reduced responsiveness of cells. These elevated insulin levels can stimulate the ovaries to overproduce androgens (male hormones), such as testosterone. The excess androgens disrupt the normal functioning of the ovaries and can result in the development of cysts.
- Disrupted hormone balance: Insulin resistance can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones in a woman’s body. Elevated insulin levels can interfere with the normal production and regulation of reproductive hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone. This hormonal imbalance can lead to irregular or absent menstrual cycles, difficulty in ovulation, and fertility issues.
- Increased androgen levels: As mentioned earlier, insulin resistance can lead to increased production of androgens, especially testosterone. High levels of androgens can cause various symptoms commonly associated with PCOS, including excessive hair growth (hirsutism), acne, and male-pattern baldness.
- Impaired glucose metabolism: Insulin resistance impairs the body’s ability to effectively use glucose for energy. As a result, the body produces even more insulin to compensate for this inefficiency. This vicious cycle can lead to further insulin resistance and worsen the symptoms of PCOS.
- Weight gain and difficulty in weight loss: Insulin resistance and PCOS are often accompanied by weight gain, particularly in the abdominal area. The excess weight can further contribute to insulin resistance and exacerbate the symptoms of PCOS. Additionally, women with PCOS may find it challenging to lose weight due to the hormonal imbalances and insulin resistance.
- Increased risk of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes: Insulin resistance is a precursor to metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. Women with PCOS and insulin resistance are at a higher risk of developing these metabolic disorders.
In conclusion, insulin resistance plays a significant role in the development and progression of PCOS. Elevated insulin levels, hormonal imbalances, and metabolic disturbances contribute to the symptoms and complications associated with PCOS. Understanding the relationship between insulin resistance and PCOS is crucial for managing the condition effectively.
If you’re struggling with PCOS or want to take proactive steps to improve your health, the Fitpaa app can be a valuable tool. Fitpaa offers personalized health and fitness plans tailored to your specific needs, including PCOS management. With Fitpaa’s expert team of fitness coaches, nutritionists, and doctors, you can receive guidance and support to optimize your metabolism, achieve your fitness goals, and improve your overall well-being. Download the Fitpaa app now and take control of your health journey!