Does Fatty Liver Affect the Absorption of Nutrients?
Understanding Fatty Liver
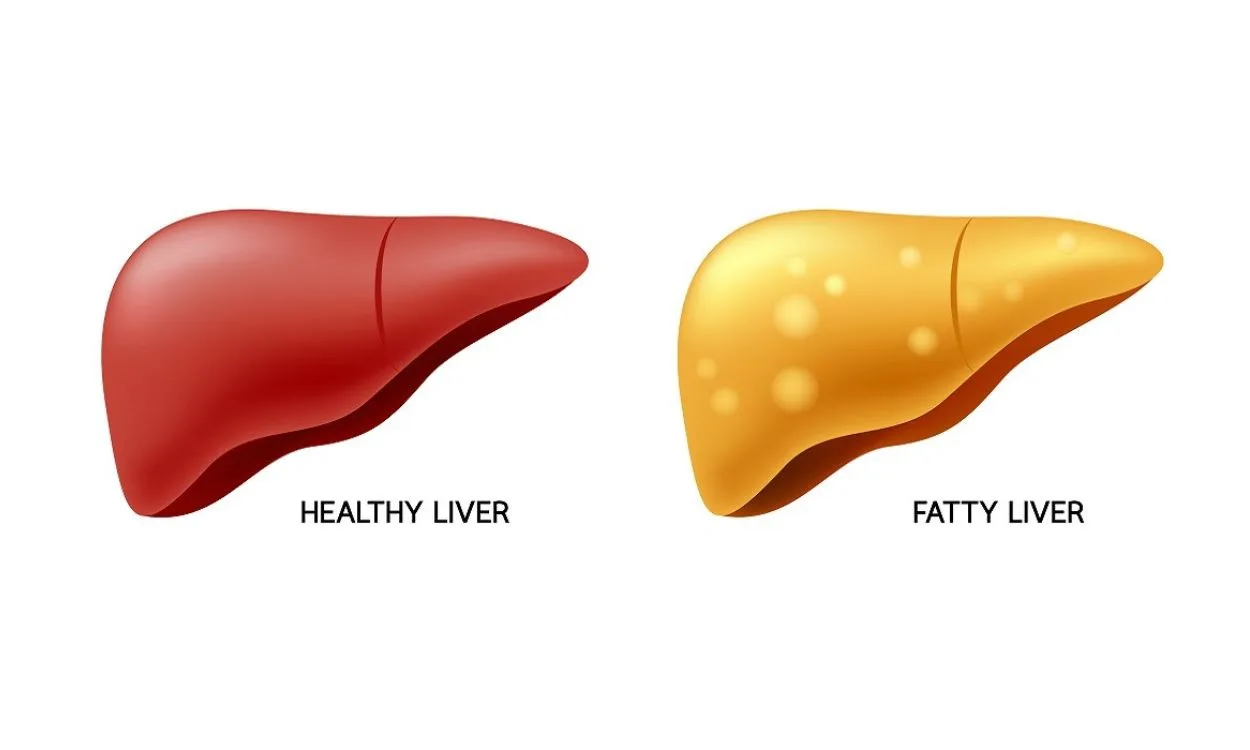
- Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells. It can be caused by alcohol consumption (alcoholic fatty liver disease – AFLD) or non-alcoholic factors (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease – NAFLD).
- NAFLD is becoming increasingly common due to sedentary lifestyles, poor dietary choices, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. It is estimated that about 25-30% of the Indian population is affected by NAFLD.
Impact on Nutrient Absorption
- Fatty liver can impair the body’s ability to absorb and utilize essential nutrients, which can lead to various health complications.
- The liver plays a crucial role in nutrient metabolism and storage. When the liver is affected by excessive fat accumulation, it may not function optimally, resulting in:
- Reduced absorption of fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin D, E, and K, which are essential for bone health, immunity, and blood clotting.
- Impaired metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, leading to potential deficiencies in essential macronutrients.
- Disruption of bile production, which is necessary for the digestion and absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins.
Nutritional Implications of Fatty Liver
- Individuals with fatty liver may experience deficiencies in key nutrients, including:
- Vitamin D: Essential for calcium metabolism, bone health, and immune function.
- Vitamin E: An antioxidant that protects cells from damage and supports immune function.
- Vitamin K: Crucial for blood clotting and bone health.
- B-complex vitamins: Including B12, B6, and folate, which are essential for energy production and nerve function.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Important for heart health and reducing inflammation.
Mitigating Nutritional Deficiencies
- It is imperative for individuals with fatty liver to focus on a nutrient-dense diet that includes:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Lean protein sources such as fish, poultry, and legumes.
- Healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and seeds.
- Whole grains and complex carbohydrates for sustained energy.
- Supplementation may be recommended under the guidance of a healthcare provider, especially for vitamin D, vitamin E, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Seeking Professional Guidance
- Individuals with fatty liver should work closely with healthcare professionals, including nutritionists and hepatologists, to develop a personalized dietary and lifestyle plan that addresses nutrient absorption and liver health. Regular monitoring and adjustments may be necessary to ensure optimal nutrition and liver function.
Fitpaa: Your Partner in Health and Wellness
- If you have been diagnosed with fatty liver or are concerned about your liver health, it is crucial to prioritize holistic well-being. Fitpaa’s comprehensive approach to health and fitness can support individuals in managing their conditions and achieving their wellness goals with guaranteed results.
- With personalized Fitpaa Capsules tailored to individual metabolism and health objectives, users can benefit from a blend of medical therapy, nutrition therapy, exercise therapy, and behavioral guidance to optimize their overall health, including liver function.
- The Fitpaa app offers real-time guidance, expert consultations, and goal-oriented services with lifetime validity, ensuring that users receive the necessary support and resources to improve their health and vitality.
- By leveraging the latest research in lifestyle medicine and behavioral therapy, Fitpaa empowers individuals to strengthen their organ systems, including liver health, and work towards a healthier, more vibrant life.
- To embark on your journey towards improved health and vitality, download the Fitpaa app and experience the transformative potential of personalized health and fitness solutions.