How Fatty Liver Influences Your Circulatory System: Insights and Solutions
Understanding Fatty Liver and its Impact on the Circulatory System
Fatty liver disease, known medically as hepatic steatosis, occurs when excess fat builds up in the liver. While often linked with excessive alcohol consumption, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is becoming increasingly common due to sedentary lifestyles and poor dietary choices, particularly in urban Indian settings.
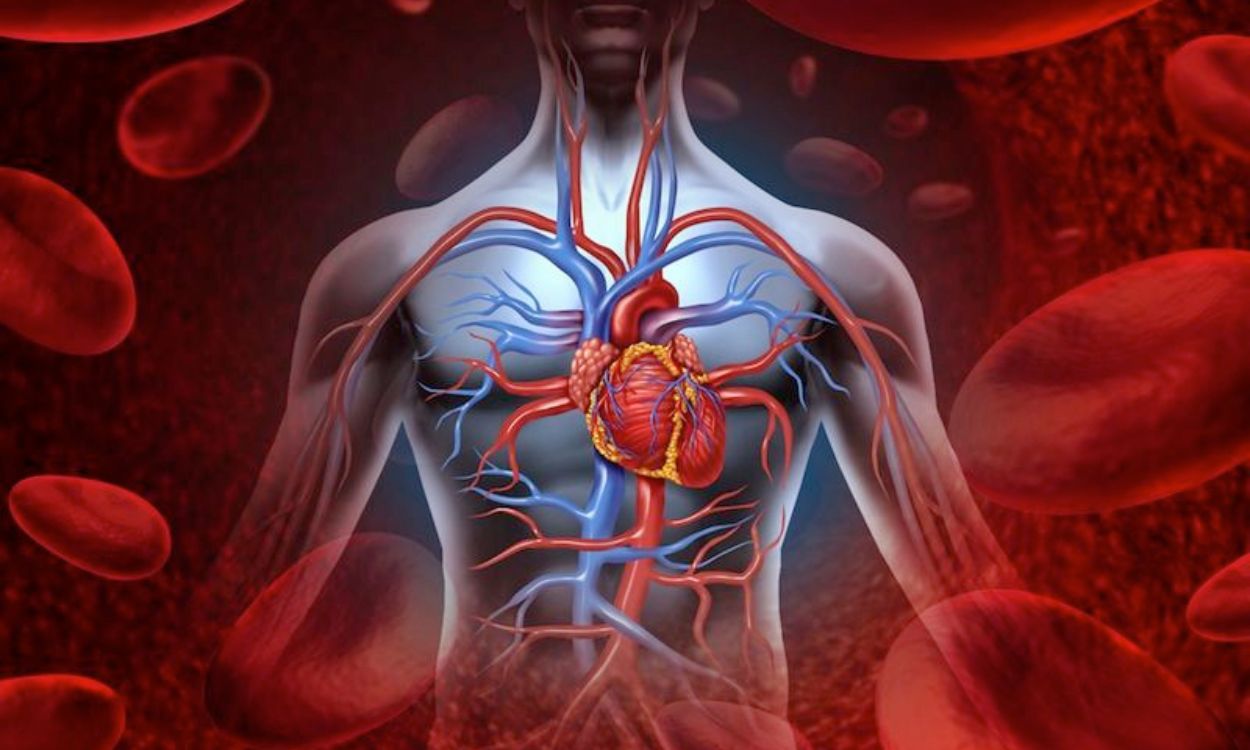
The liver plays a crucial role in the body’s overall function, affecting not just digestion and detoxification, but also impacting the circulatory system in several ways. Here’s how:
1. Increased Risk of Atherosclerosis: Fatty liver often accompanies metabolic syndromes that include high cholesterol and triglycerides. These fat particles can circulate in the blood, leading to deposits in the arteries, which may result in atherosclerosis, a condition where arteries become narrowed and hardened.
2. Hypertension: The liver’s inability to properly manage fats can lead to an increase in blood pressure. The presence of excess fat in the liver can cause resistance to insulin, contributing to increased blood pressure levels—a key factor in circulatory system issues.
3. Elevated Risk of Heart Disease: There is substantial evidence linking fatty liver with increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. The inflammation and oxidative stress caused by fatty liver can extend to the heart, increasing the likelihood of coronary artery disease.
4. Impaired Blood Flow: A healthy liver ensures the efficient flow of blood through the body. However, when compromised, it can lead to portal hypertension, where blood pressure in the liver’s main vein becomes too high, adversely affecting blood circulation.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
Understanding these connections is the first step towards prevention and management. Here are some practical steps that can help mitigate the risks:
– Healthy Diet: Embrace a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Reducing saturated fats, sugars, and alcohol can significantly lower fat accumulation in the liver.
– Regular Exercise: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise weekly. This helps in managing weight, reducing liver fat, and improving overall cardiovascular health.
– Regular Monitoring: Regular health check-ups and liver function tests can detect fatty liver early, allowing for timely intervention.
Why Fitpaa is Your Ideal Health Partner
After understanding the profound effects of fatty liver on the circulatory system, you might wonder about sustainable solutions. This is where Fitpaa emerges as a transformative tool in your health journey.
Comprehensive Health Assessment: Fitpaa’s AI-driven metabolism monitoring technology provides a detailed health analysis, identifying potential risks and offering actionable insights into your metabolic health.
Personalized Fitpaa Capsule: Tailored to your unique lifestyle and health goals, the Fitpaa Capsule combines medical nutrition therapy, exercise routines, and cognitive behavior strategies to optimize liver function and enhance circulatory health.
Guided Support and Real-Time Tracking: With Fitpaa, you’re never alone. The app offers real-time guidance, habit-building techniques, and motivational nudges to keep you on track. The integrated fitness planner, nutritionist, and physician consultations ensure you have a holistic support system at your fingertips.
Join the Fitpaa Community
Join thousands of others who have revolutionized their health with Fitpaa. Experience a seamless blend of technology, personalized care, and expert guidance to not just tackle fatty liver but to elevate your overall health and wellness. Download the Fitpaa app today and take the first step towards a healthier, happier you.
By combining insightful health information with practical lifestyle strategies, this article not only addresses the query of how fatty liver affects the circulatory system but also seamlessly integrates Fitpaa’s offerings, encouraging downloads and engagement.